Edit Content
Jacksonville Florida
Your trusted financial team
- Serving St. Augustine
- Serving Jacksonville
- Serving All of the United States Remotely
- [email protected]
- (904) 323-2069
FOLLOW US
Your trusted financial team
Did you know your Social Security benefits in retirement could be 100% tax-free?
Perhaps you didn’t even know Social Security would be taxable as many of you paid into the system for decades!
Today we will unpack how Social Security retirement benefits are taxed, and most importantly how to reduce taxes on those benefits in retirement.
A few notes for the listeners:
Provisional Income / Social Security Tax Rates for 2023
Individual
Married Filing Jointly
A helpful Kitces.com article
If you have already begun drawing Social Security, you might be surprised to learn taxes are owed on some of your benefits! After all, you’ve been paying into the system via payroll taxes, so why is your benefit also taxable? If you have yet to begin drawing Social Security yet, you can never say you weren’t told! As a result, I’m often asked if there is a way to reduce taxes on your Social Security benefits. This blog post will unpack how Social Security taxes work and how to reduce taxes on your benefits. Make sure to join our newsletter so you don’t miss out on any of our retirement planning content (click here to subscribe!). I hope you find this article helpful!

The Social Security Act was signed into law by President Roosevelt in 1935! It was designed to pay retired workers over the age of 65. However, life expectancy at birth was 58 for men and 62 for women! Needless to say, there weren’t a huge number of retirees collecting benefits for very long. As people began to live longer, several key provisions were added later. One was increasing the benefits paid by inflation, also known as Cost of Living Adjustments (COLA). Another was changing the benefits from a lump sum to monthly payments. Ida Fuller was the first to receive a monthly benefit, and her first check was $22.54! If you adjust this for inflation, that payment would be worth $420.15 today! If you compare this to the average Social Security benefit paid to retirees of $1,782/month, those early payments were chump change!
According to data from 2021, life expectancy at birth is 73.5 years for men and 79.3 years for women! In 2008, there were 39 million Americans over age 65. By 2031, that number is projected to reach 75 million people! We’ve all heard of the notion that older (more expensive) workers are being replaced by younger (less expensive) workers. While taxable wages are going down and retirees collecting benefits are increasing, the result is a strain on the system.
Social Security benefits are actually funded by taxpayer dollars (of course). If you look at a paystub, you will see FICA taxes withheld automatically. FICA stands for Federal Insurance Contributions Act and is the tax revenue to pay for Social Security and Medicare Part A. The Social Security portion is 6.2% for the employee and 6.2% for the employer, up to a maximum wage base of $160,200. So, once you earn above $160,200 you likely will notice a “pay raise” by way of not paying into Social Security any longer. Medicare is 1.45% up to $200,000, and then an additional 0.9% for wages above $200k (single filer) or $250k (married filing jointly).
Up until 2021, FICA taxes have fully covered Social Security and Medicare benefits. However, because of the challenges mentioned earlier, FICA taxes no longer cover the benefits paid out. The good news is there is a Trust Fund for both Social Security and Medicare for this exact reason. If there is a shortfall, the trust fund covers the gap. The big challenge is if nothing changes, Social Security’s trust fund will be exhausted in 2034 and Medicare’s in 2031.
The first concept to understand is that the % of your Social Security that will be taxable is based on your “combined income,” also known as provisional income. If your combined income is below a certain threshold, your entire Social Security check will be tax-free! If your combined income is between a certain threshold, up to 50% of your Social Security benefit will be taxable. And finally, if your income is above the final threshold, up to 85% of your Social Security benefit will be taxable. Here are the thresholds below.
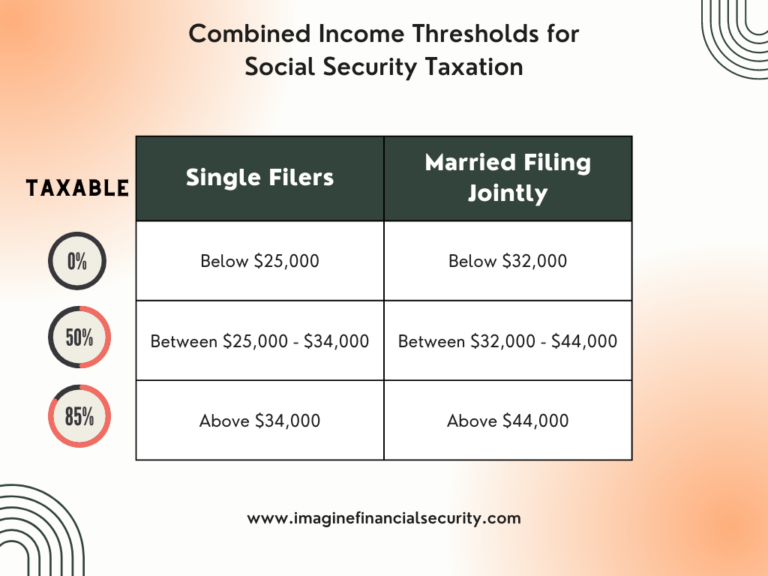
The basic formula is to take your Adjusted Gross Income (NOT including Social Security), add any tax-exempt interest income, and then add in 50% of your Social Security benefits.
If you are retired, you likely will have little to no earned income, unless you are working part-time. Your adjusted gross income will be any interest income, capital gains (or losses), retirement account distributions, pensions, etc. This is important to note because not all retirement account distributions are treated the same! Additionally, capital gains can be offset by capital losses. So even though your cash flow might exceed these numbers significantly, you still might be able to reduce or even eliminate how much tax you pay on your Social Security Income.
Client A has the following cash flows:
The combined income in this scenario is $80,000.
Half of Social Security ($20,000) + $50,000 IRA distribution + $10,000 municipal bond income = $80k.
Notice how the municipal bond income is added back into the calculation! Many clients try to reduce taxes on their bond interest payments by investing in municipal bonds. However, it’s important to note how this interest income might impact other areas of tax planning.
In this scenario, 85% of their Social Security benefit will be taxable.
The first $32,000 of income doesn’t trigger any Social Security taxes.
The next $12,000 will include 50% ($6,000)
And finally, the amount over $44,000 ($36,000) includes 85% (85% * $36,000 = $30,600).
$6,000 + $30,600 = $36,600
If you divide $36,600 by the $40,000 Social Security benefit, it gives you 91.5%. However, a maximum of up to 85% of the Social Security benefit is taxable, so in this case, they are capped at 85% and $34,000 will be their “taxable Social Security” amount.
Client B has the following cash flows:
Client B’s provisional income is only $24,000!
Half of Social Security ($20k) + $0 retirement account distributions + $4,000 interest income = $24,000
As you can see, the Social Security benefits are identical to client A. However, the $50,000 retirement account distribution is from a Roth account, and in this case, it was a tax-free distribution. And finally, the interest income was way down because the client elected to reduce their bond allocations in their taxable account and instead owned them inside of their IRAs (which is not taxable).
So despite having essentially identical cash flows, Client B enjoys 100% of their Social Security check being tax-free! In other words, they have reduced their taxable income by $34,000 compared to client A!
A huge challenge arises for clients who are under the max 85% threshold. Each dollar that is added to their retirement income will increase how much Social Security is taxed! If someone is in the 50% range and they take an additional $1,000 from a Traditional IRA, they will technically increase their adjusted gross income by $1,500! $1,000 for the IRA distribution and $500 for taxable Social Security income!

So while you shouldn’t let the tail wag the dog, you should absolutely begin mapping out how you can make your retirement income plan as tax efficient as possible! Here are a few ways to reduce your “combined income” and thus reduce your taxes on Social Security payments.
Simply put, a Roth conversion allows you to “convert” all or a portion of your traditional IRA/401k/403b to a Roth account. Of course, you will have to pay taxes on the amount converted, but all of the growth and earnings can now be tax-free!
This is perhaps one of the most impactful strategies you can incorporate! However, you must start this strategy at the right time! If you are still employed and perhaps at the peak of your earnings, you may not benefit from Roth conversions…yet. However, if you recently retired and have yet to begin the Required Minimum Distributions (RMDs), you might find it to be a valuable strategy if you execute it properly.
One of our most recent podcast episodes is about this topic; you can listen to it here.
The RMD trap is simply the tax trap that most people with Traditional IRAs or 401ks run into. In the early years of retirement, your RMD starts out quite low because it’s based on your life expectancy according to the IRS. However, each year the amount you are required to withdraw increases. By the time you are in your 80s and even 90s, the amount you are taking out could exceed what you need for cash flows! But despite needing it for income or not, you have to withdraw it to avoid the dreaded penalties, and this could push you into higher tax brackets later in retirement. And of course, this could also increase the taxation of your Social Security check!
Roth conversions help with this, but it could also help to try to even out the distributions! Instead of just waiting for the RMDs to balloon, perhaps you devise a better withdrawal strategy to target a certain tax bracket threshold throughout your retirement.
You may have heard of the term “Asset Allocation,” which involves careful selection of asset classes that align with a portfolio’s objectives. In essence, what % of stocks, bonds, real estate, and cash does the portfolio hold? Asset Location involves selecting which accounts will own those asset classes in order to maximize tax efficiency and time horizon.
When we looked at the Social Security examples earlier, you probably noticed Client B had less taxable interest income. This is because they elected to reduce the amount of fixed income in their “taxable” account, and moved those assets into their IRAs.
Alternatively, you might have a longer time horizon with some of your accounts, like a Roth IRA. Given Roth’s tax-free nature and the NO RMDs, this account is a great “long-term” bucket for retirement income planning. As a result, you might elect to have this account ultra-aggressive and not worry much about capital gains exposure, etc.
You should take advantage of the tax characteristics of different “buckets” for retirement income planning. Not all of your investment accounts should look identical in that sense.
Perhaps one of the most UNDERRATED strategies is tax loss harvesting. Oftentimes when the market is down, people bury their heads in the sand hoping that things will improve one day. And this is certainly better than selling out and moving to cash! However, there is one step many people miss: realizing losses when the markets are down. These losses can then be used to offset capital gains, and even reduce your ordinary income!
I oftentimes hear pushback that people don’t want to offload investments at a loss because they were trained to “buy low and sell high.” This is a great point, but with tax loss harvesting, after the loss is realized, you then turn around and replace the investment you sold with something similar, but not “substantially identical.” That way, you avoid the Wash-Sale rule so you can recognize the tax loss, but you stay invested by reallocating funds into the market.
Episode 19 of The Planning for Retirement Podcast is all about this topic and you can listen to it here!

Okay, so you missed the boat on Roth conversions, and you are already taking RMDs from your accounts. Qualified Charitable Distributions, or QCDs, allow for up to $100,000/year to be donated to charity (qualified 501c3) without recognizing any taxable income to the owner! Of course, the charity also receives the donation tax-free, so it’s a win-win! I oftentimes hear of clients donating to charity, but they are itemizing their deductions. Almost 90% of taxpayers are itemizing because of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017. QCDs can be utilized regardless if you are taking the standard deduction or not! And the most powerful aspect of the QCD is that it will reduce your RMD dollar for dollar up to $100k.
Let’s say your RMD for 2023 is $50k. You typically donate $10k/year to your church but you write a check or donate cash. At the end of most tax years, you end up taking the standard deduction anyways, so donating to charity doesn’t hurt or help you.
Now that you’ve learned what a QCD is, you go to the custodian of your IRA and tell them you want to set up a QCD for your church. You fill out a QCD form, and $10k will come out of your IRA directly to your Church (or whatever charities you donate to). Now, your RMD is only $40k for 2023 instead of $50k! In essence, it’s better than a tax deduction because it was never recognized as income in the first place!
Two important footnotes are the QCD has to come from an IRA and the owner must be at least 70.5 years old! It cannot come out of a 401k or any other qualified plan!
We wrote an entire article on QCDs (and DAFs) that you can read here.
Retirement Planning is so much more than simply what is your investment asset allocation. Each account you own has different tax characteristics, and the movement of money within or between those accounts also has tax consequences. Instead of winging it, you could save tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars in taxes in retirement if you are proactive. However, the tax code is constantly changing! In fact, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 is expiring after 2025, so unless something changes, tax rates are going up for most taxpayers. Additionally, the markets are beginning to recover, so strategies like tax loss harvesting or Roth conversions become less impactful. But, there is still plenty of time and opportunity!
Thanks for reading and I hope you learned something valuable. Make sure to SUBSCRIBE to our newsletter to receive updates on me personally, professionally, and of course, content to help you achieve financial independence! CLICK on the “keep me up to speed” button below.
-Kevin
Sometimes “hanging tight” isn’t the best solution during times of volatility. We’ve had two bear markets since the Great Recession of 2008. COVID-19 was the first, and the inflation that ensued thereafter in 2021-2022 led to the second. Tax Loss Harvesting involves selling investments when they are down in value (in a taxable account) to create a realized loss for tax purposes. You can then use these losses in current or future years (retirement) to reduce taxes!
These opportunities don’t come every year, so it’s important to take advantage while you (still) can!
I hope you enjoy this episode!
Copyright © 2020 imagine financial security. All Rights Reserved. Website by Justin Bordeaux

